
Hemp-derived CBD for Adult Seniors
Humans have been using cannabis, both marijuana and hemp, medicinally for over 10,000 years. It fell out of political favor in the United States and was banned in the 1930s and placed on the Drug Enforcement Agency’s (DEA) list of Schedule I drugs in the 1970s.
Its criminalization effectively halted all research in the United States into the plant’s potential medical benefits; however, there were still a few federally sanctioned scientific studies conducted as early as the 1950s. In 2018, the Farm Bill once again legalized hemp. Since then, there have been numerous independent scientific studies on cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Despite its full legal status, Forbes reported in 2019 that only 9% of adult seniors have tried CBD for health-related reasons. Of those who have tried it, they reported that CBD affected them in the following ways:
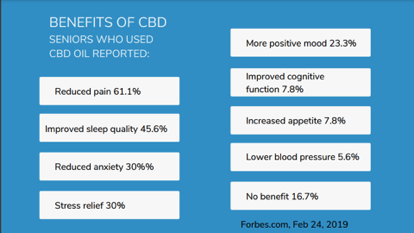
Given the potential to increase one’s health condition, why are adult seniors not joining in the CBD craze? We will attempt to dispel some of the common barriers to understanding CBD.
Understanding CBD
THC and CBD were first successfully isolated from the cannabis plant in the 1960’s by Israeli scientist Raphael Mechoulam. Mechoulam’s complete fascination with the plant drove him to study it for the next 50+ years. In the 1990’s he played a key role in the discovery of the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS helps keep the central nervous system and immune functions in homeostasis or balance. Today, experts know that your ECS impacts several major processes, including immune function, inflammation, anxiety, sleep, mood and memory. Mechoulam once said,
“One of the major effects of endogenous cannabinoids is to regulate the release of dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters. They seem to be major regulators.”
CBD is one of over 100+ active compounds found in the Cannabis plant. THC is another active compound and the most well-known, thanks to its psychoactive properties — it can get you “high.” In contrast, CBD is non-psychoactive and it has numerous medical benefits without giving you that “stoned” feeling.

Is CBD Legal?
CBD and THC are cannabinoids found in both the hemp and marijuana cannabis plants. The difference is that hemp plants have less than 0.3 percent THC, while marijuana plants have much higher levels of THC.
After being banned for decades, the 2018 Federal Farm Bill legalized hemp and hemp-derived products. This means that is now legal to grow, process, sell, and consume hemp-derived CBD in all 50 states — without the hefty tax placed on marijuana products. Medical marijuana cards are not necessary to purchase hemp-derived CBD. Products can also be shipped legally across state boundaries.
As for the marijuana plant, its path to legalization continues to spread around the country. Currently, 15 states and Washington, DC, have legalized marijuana for adults over the age of 21. Additionally, 36 states have legalized medical marijuana — meaning that a majority of Americans now have some form of access to marijuana, whether medically or recreationally.
It is important to reinforce the difference between hemp and marijuana products and that is hemp-derived CBD products can contain only trace amounts of THC (less than 0.3%) — generally not enough to cause a high or register on a drug test, though it is possible. All CBD products from Fremont Botanicals are from the hemp plant!
Hemp-derived CBD full spectrum, broad spectrum or isolate
There are 100+ known cannabinoids in the hemp plant. Cannabinoids work better together than they do alone — known as the entourage effect. However, given that people have differing needs and physiologies, manufacturers created three different forms of CBD; full-spectrum, broad-spectrum and isolate. Your choice of CBD form determines what you get in your product along with the actual CBD.
- Full-spectrum CBD contains all of the naturally available compounds of the cannabis plant, including trace amounts of THC – less than 0.3 percent by the dry weight.
- Broad-spectrum CBD has all of the naturally occurring compounds, except all of the THC is removed.
- CBD isolate is the purest form of CBD. The CBD is isolated from the other compounds of the hemp plant and contains no THC
So, which should you choose? Some people prefer full-spectrum because they want the benefits of the whole hemp plant’s benefits — with all the cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids working in synergy. Others choose broad-spectrum because they want all the cannabinoids, minus THC, terpenes and flavonoids. Some people prefer CBD isolate for its therapeutic effects without any other compounds. Others also choose broad-spectrum or isolate because they are very sensitive to THC or their jobs require drug testing on a regular basis.
What are terpenes and flavonoids?
Like cannabinoids, terpenes are a plant compound reported to have therapeutic and health-boosting benefits. Terpenes also give plants their unique flavor.
Flavonoids are compounds found in green tea and certain fruits that have been found to protect against disease.
How do I choose the best CBD brand for my needs and avoid false advertising?
Look at the product label for ingredients. Make sure the product actually has CBD or cannabidiol in it. Keep in mind that some products will list CBD as hemp extract instead of CBD oil.
Products that have no mention of cannabidiol or hemp extract and only list hemp seeds, hempseed oil, or Cannabis sativa seed oil. Hemp seeds do not contain CBD.
Check the ingredient list to make sure you are not allergic to anything. If you are buying a CBD oil, the product will include a carrier oil to stabilize and preserve the CBD and help your body absorb it. That is why one of the main ingredients of the product may be grapeseed oil, MCT oil, olive oil, or even cold-pressed hempseed oil. A CBD oil or an edible might also contain a natural or artificial flavoring or coloring.

If you are buying a broad- or full-spectrum product, it should also list the cannabinoids and terpenes included, although these are often included in the certificate of analysis (COA).
Understanding the COA or third-party testing of CBD products
A reputable CBD product will come with a COA. That means it has been third-party tested by an independent laboratory. The COA contains the test results conducted by the laboratory, such as the amount of each cannabinoid present and any residual chemicals, microbes and heavy metals. You may be able to access the COA by scanning the QR code and/or batch number on the product. Many product websites or retailers also have the COA available. If the website does not have a COA, email the company and ask to see the COA. There are few key factors:

Cannabinoid profile:
If your product is full- or broad-spectrum, look for a list of cannabinoids and other compounds. Cannabinoids like cannabidiol acid (CBDA), cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerol (CBG), and cannabichromene (CBC) should be on the list.
Additional lab charts
Look for heavy-metal and pesticide analyses, as well. You can determine if a certain contaminate is detected at all. If so, is it within a safe limit for ingestion? Check the status column of these charts and make sure it says “pass.”
How to determine CBD concentration and dosage
There is a lot of confusion when trying to determine the amount of CBD in a product and how much is in each dose. A number often displayed on the package is the amount of CBD in milligrams (mg) for the entire product; not the amount of CBD per dose. For example, if you have a bottle of 500mg CBD oil and there are 30 servings per bottle, this means that each serving contains 16.7mg of CBD per serving. Or you might have a package of gummies with 300mg of CBD. If there are 30 gummies in the package, you will get 10mg of CBD per gummy.
What is the correct dosage?
The amount of CBD you should take depends on a range of factors, including:
- your body weight
- the condition you are treating
- your individual body chemistry
- the concentration of CBD in each pill, capsule, drop, or gummy.
Put simply, there are a ton of variables that go into deciding how much CBD to take. Before trying CBD, be sure to talk to your doctor about an appropriate dosage and any potential risks.
If your doctor does not provide a recommendation, it is best to start with a smaller dosage and gradually increase it. This could mean starting with as little 5mg a day. After one or two weeks, increase this amount by 5mg. Continue titrating until you feel that it is effectively treating your symptoms. Still, do not exceed the recommended dosage for your weight or severity of your condition without talking to your doctor first. In general start with a low dosage and go slow with increasing your dose.

Is it safe? Does it interact with other medications?
Current research shows that CBD is generally safe and has few, if any, minor side effects. But there is one big caveat: CBD does have the potential to interact with some medications. The concern has to do with how the body metabolizes certain substances. Before trying CBD, we recommend that you talk to your doctor or pharmacist about all of the vitamins, supplements, and prescription and over-the-counter medications you are taking. They may be able to help determine a CBD product, dosage, and schedule that will be safe to take alongside your existing medications. For some situations, your doctor may want to monitor blood plasma levels. Do not stop any of your medications to try CBD, unless your doctor says it is safe to do so.
Look for the grapefruit warning
Studies are still ongoing to determine potential interactions between CBD and specific medications. In general, there is one rule of thumb that can help consumers: ask your doctor if your medication has a “grapefruit warning” on the label. Some common prescriptions that have a grapefruit warning include blood thinners and blood pressure medications.
Even if your medication does have a grapefruit warning, your doctor might be able to formulate an individualized plan that includes CBD through the close monitoring of medication levels in your system. That way, you can use both your prescription and CBD as a therapy.
Potential side-effects
Common side effects include increased fatigue, change in appetite, change in weight and drowsiness.
Bottom line
Keep in mind that topical CBD, like lotions, creams, and salves may be a less invasive alternative to CBD oils. Unlike oils, edibles, and vaping solutions, topicals typically do not enter the bloodstream (as long as they are not a transdermal solution intended to do so).
Always consult your doctor first before trying CBD, especially if you have a health condition and are taking medications. Do not stop taking your prescription medications to try CBD, unless you have the go-ahead from your doctor.
How do I take CBD?

CBD is available in several different forms. This allows people to tailor their method of use to their specific need. Here are the most common forms of CBD:
Oils and tinctures
These liquids, usually oils, are infused with CBD and placed under the tongue with a dropper. The oral mucosa is full of tiny capillaries that absorb the compounds quickly. Oils and tinctures are a good choice for anyone who cannot take pills or capsules.
Balms, roll-on and lotions
CBD-infused topicals are used to treat muscle and joint pain. They can also treat some skin conditions, like eczema and psoriasis.
Capsules and pills
CBD capsules and pills are used for systemic treatment of seizure disorders and digestive issues. One drawback with capsule is the delay from ingestion to the onset of the desired effect.
Edibles
Edibles include chocolates, honey and gummies. Gummies are one of the most popular ways to take CBD. They are affordable, portable, discrete, and tasty. CBD-infused chocolates are also great for people with a discerning taste and sensitive pallet.
Patches
CBD patches are an extremely efficient method to deliver CBD. Designed to be a transdermal solution, about 50% of what is applied to the skin reaches the bloodstream and Endocannabinoid System (ECS) without permeation enhancers. As a bonus, CBD also activates the skin cells directly (without needing it to travel through the blood), which could be very beneficial for people with skin disorders.

Vaping
Inhaling vaporized CBD oil is the fastest way to experience its effects. Compounds are inhaled and absorbed directly from the lungs into the bloodstream. The jury is still out, though, on whether vaping CBD does damage to delicate lung tissue. Proceed with caution if you choose to vape CBD.
Inhaler
Consistent precise dosing with rapid uptake into the human circulatory system. Micell Tech is a sub-nanoparticulate, fully water-soluble with 7x the bio-availability and 10x the absorption of regular CBD oil.
Key Takeaways

CBD has been used medicinally for thousands of years. Current studies indicate that CBD may have many benefits that may improve your health, even when used alongside other western medications! Remember to always consult your doctor first before trying CBD, especially if you have a health condition and are taking prescription medications. And do not stop taking your prescription medications unless you have approval from your doctor!
Remember that aging does not have to be traveled alone. Thank you for taking the time to read this blog and we sincerely hope you find CBD helpful.

